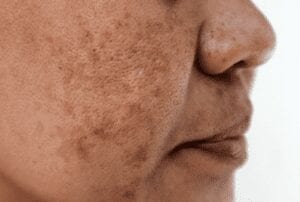
Melasma is a chronic condition that primarily affects healthy women of childbearing age. It is believed that a combination of sun exposure, hormones, and genetic susceptibility leads to developing the characteristic blotchy skin associated with Melasma. Traditionally, its treatment has been based on four distinctly different but interrelated modalities:
Avoidance of UV exposure;
Topical regulation of melanocytic activity;
Selective light-based and laser-based photothermolysis of melanocytes or melanin; and
Chemical or mechanical exfoliation.
Before starting any protocol to lighten the skin, it is important to understand the primary causes of most hyperpigmentation: unprotected sun exposure and glycation. What is glycation, you ask? Glycation is a physiological reaction in the body when simple sugar molecules such as fructose or glucose become attached to proteins or lipid fats without the moderation of an enzyme, which results in rogue formation molecules known as advanced glycation end products (AGEs). This leads to several health problems, including skin discoloration and inflammation.
Much of what is known about glycation’s ill effects come from diabetes research: The connective-tissue damage and chronic inflammation resulting from diabetics’ sustained high blood sugar can lead to debilitating conditions, such as cataracts, Alzheimer’s, vascular tightening, and diseases of the pancreas and liver. Simply put – SUGAR is enemy #1!
The following ingredients are healthy AND very effective alternatives to synthetic hydroquinone. Be sure to look for them on your product labels:
Treating Melasma with Sunshine Botanicals